Glutathione is a tripeptide antioxidant made from glycine, cysteine, and glutamic acid, produced by the liver to support immune function, protein synthesis, and detoxification.
- Email : info@skinvibesclinic.com
- Santacruz (W), Mumbai – 400 054
- Call : 91 + 9833-807-003
Glutathione IV Therapy
Glutathione IV Therapy
Glutathione IV therapy has gained popularity in recent years as a wellness treatment aimed at enhancing the body's natural defenses and promoting overall health. This article explores what Glutathione IV therapy entails, who might benefit most from it, its potential advantages, associated risks, and answers to common questions.
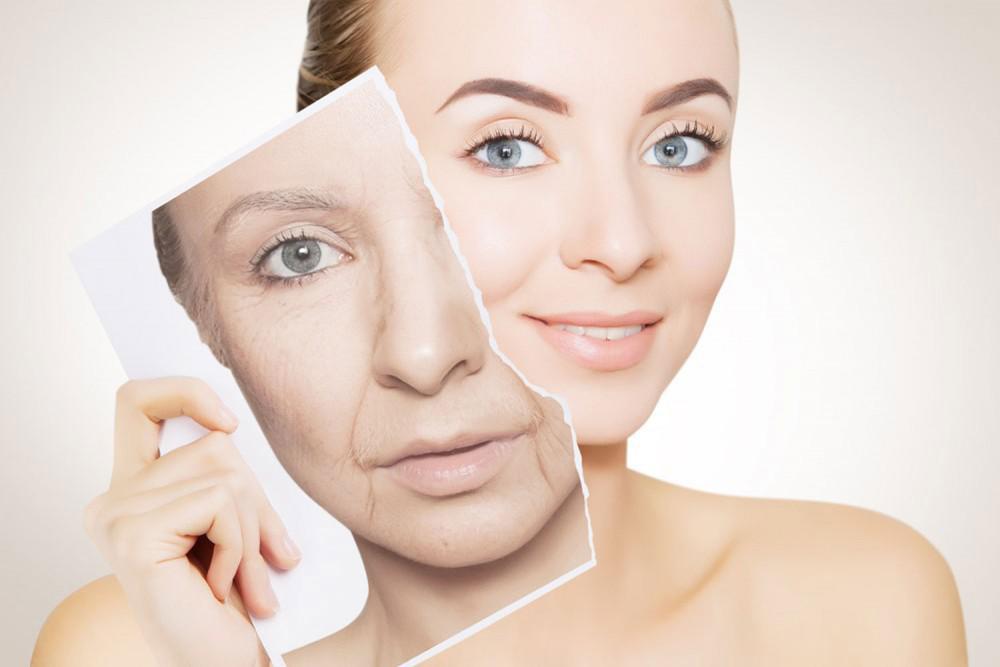

What is Glutathione IV Therapy?
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant naturally produced by the body, composed of three amino acids: cysteine, glutamate, and glycine. It plays a crucial role in combating free radicals—unstable molecules that can damage cells—and aiding in detoxification processes, such as breaking down pollutants, drugs, and other toxins. Levels of glutathione can decline with age, stress, or certain health conditions, leading to increased oxidative stress.
Glutathione IV therapy involves administering this antioxidant directly into the bloodstream via an intravenous drip, bypassing the digestive system for higher absorption rates compared to oral supplements. This method ensures that the body receives a concentrated dose, making it more effective for therapeutic purposes. It's often used in clinical settings or mobile IV services to support liver function, immune health, skin vitality, and hair health.

Who Are the Best Candidates for Glutathione IV Therapy?
Not everyone needs Glutathione IV therapy, but it may be particularly suitable for individuals experiencing symptoms of low glutathione levels or specific health challenges. Ideal candidates include:
- Those with chronic fatigue or low energy: People dealing with persistent tiredness, brain fog, or sleep issues due to oxidative stress.
- Individuals with liver conditions: Such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease or exposure to toxins like alcohol, where glutathione supports detoxification and improves liver enzyme markers.
- People with autoimmune or inflammatory disorders: Including rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, or psoriasis, as it may help reduce inflammation and support immune balance.
- Aging adults or those seeking anti-aging benefits: To combat oxidative damage associated with aging, dementia, or skin and hair concerns like dull complexion, wrinkles, or thinning hair.
- Patients with chronic illnesses: Such as cancer, HIV/AIDS, type 2 diabetes, Parkinson's disease, heart disease, or epilepsy, where glutathione levels are often depleted.
- Individuals focused on skin and hair health: Those with uneven skin tone, hyperpigmentation, dull skin, hair loss, or brittle hair seeking brighter, healthier skin and stronger hair.
- Athletes or those recovering from trauma: To aid in muscle recovery, reduce oxidative damage from exercise, or support healing after injury.
It's gender-neutral and suitable for most adults, but candidates should consult a healthcare provider to ensure it's appropriate, especially if they have underlying conditions or are pregnant/breastfeeding. A quiz or assessment from a clinic can help determine suitability.
Benefits of Glutathione IV Therapy
Glutathione IV therapy offers a range of potential benefits backed by research and clinical observations, primarily due to its antioxidant and detoxifying properties. Key advantages include:
- Detoxification and Liver Protection: It helps neutralize toxins, protecting the liver from damage caused by alcohol, pollutants, or medications. Studies show improved liver function tests in patients with liver disease.
- Immune System Boost: By reducing oxidative stress, it enhances immune response, potentially helping fight infections, autoimmune diseases, and even reducing symptoms in conditions like autism or respiratory issues.
- Skin Brightening and Anti-Aging: Popular for evening skin tone, reducing dark spots, and promoting a youthful glow by inhibiting melanin production. It protects skin cells from oxidative damage, reducing signs of aging like wrinkles, fine lines, and dullness, and improves conditions like acne, eczema, or psoriasis for a radiant complexion.
- Hair Health Improvement: Glutathione supports hair follicles by reducing oxidative stress, which can contribute to hair loss or thinning. It may strengthen hair, improve scalp health, reduce brittleness, and promote shinier, healthier-looking hair, particularly beneficial for those with hair damage from environmental factors or aging.
- Increased Energy and Reduced Fatigue: Users report higher energy levels, better concentration, and relief from chronic fatigue by combating cell damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: May alleviate pain, improve mobility in peripheral artery disease, and reduce symptoms of Parkinson's or insulin resistance in older adults.
- Support for Chronic Conditions: It may prevent nerve damage from chemotherapy, aid in weight management for obese individuals, and protect against cell damage in diabetes or cystic fibrosis.
Results can vary, but many notice improvements in skin radiance, hair vitality, and overall well-being after a few sessions.
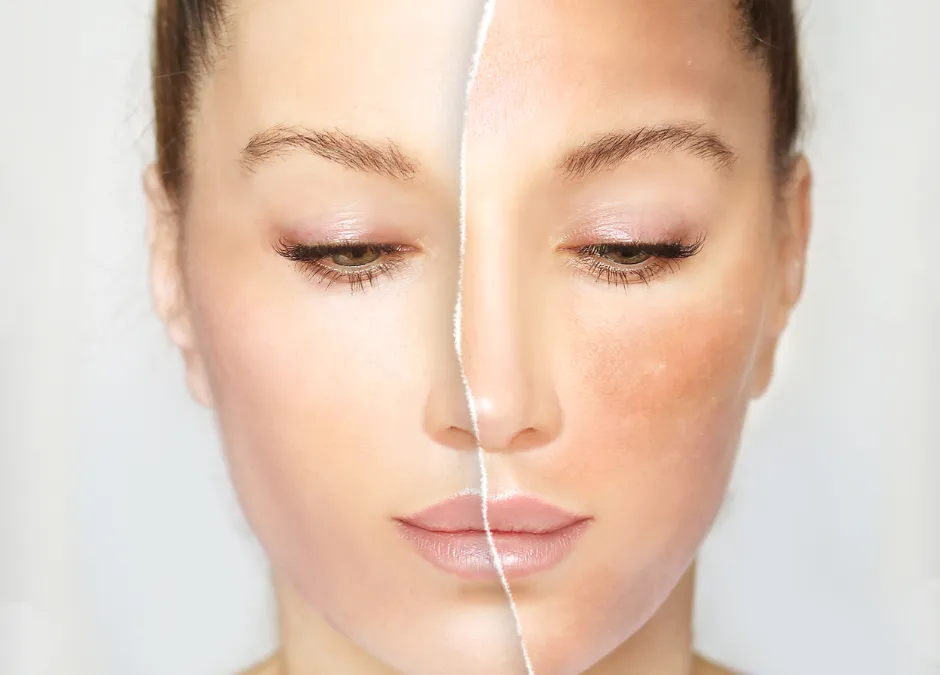

Risks and Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, Glutathione IV therapy isn't without risks, and it's not FDA-approved for uses like skin lightening. Potential side effects include:
- Common Mild Reactions: Nausea, diarrhea, bloating, stomach cramps, or abdominal discomfort, especially with high doses.
- Allergic Responses: Rare but possible, including rash, itching, or severe reactions like anaphylaxis.
- Organ Toxicity: Long-term or high-dose use may harm the kidneys, liver, or nervous system, as warned by regulatory bodies like the Philippine FDA.
- Other Concerns: Lowered zinc levels with prolonged use; asthma attacks if inhaled (though IV is different); potential interactions with medications or supplements.
- Unknowns for Certain Groups: Safety during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or in children is not well-established.
Experts recommend medical supervision, starting with low doses, and avoiding it if you have asthma, G6PD deficiency, or are on certain drugs. Always disclose your medical history to a provider.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is glutathione?
-
What are the signs of glutathione deficiency?
Common symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, dry/flaky skin, frequent infections, eczema, jaundice, hair thinning, brittle hair, or increased susceptibility to colds and flu.
-
How does glutathione IV therapy compare to oral supplements?
IV therapy bypasses digestion for 100% absorption, avoiding GI issues like bloating from pills, and provides faster, more potent effects.
-
Can glutathione help with skin and hair health?
Yes, it protects skin cells from free radical damage, reduces dark spots, evens tone, and improves conditions like acne, eczema, or psoriasis for a brighter appearance. For hair, it strengthens follicles, reduces hair loss, improves scalp health, and enhances hair shine and resilience.
-
How often can you get glutathione IV treatment?
Frequency varies; typically 1-2 sessions per week initially for 4-6 weeks, then maintenance monthly. Consult a doctor based on your goals.
-
What are the differences between glutathione and NAC?
NAC is a precursor that boosts glutathione production and supports respiratory/mental health, while glutathione directly provides antioxidant protection for immunity, skin, hair, and cell repair.
-
Can you combine vitamins with glutathione IV?
Yes, blending with vitamins (e.g., Vitamin C) may enhance benefits like brain health, skin radiance, or liver support, but check with a provider for compatibility.
-
Is glutathione IV safe for heavy trauma recovery?
It can aid healing by protecting cells from free radicals post-trauma, but consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment.
For personalized advice, always consult a qualified healthcare professional before starting Glutathione IV therapy.
